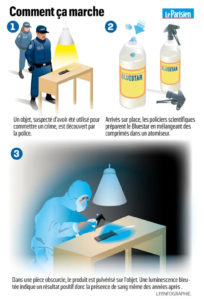
How does the scientific police work?
How does the scientific police work?
(Le Mag de France Bleu Poitou)
(France bleu: January 21, 2022)
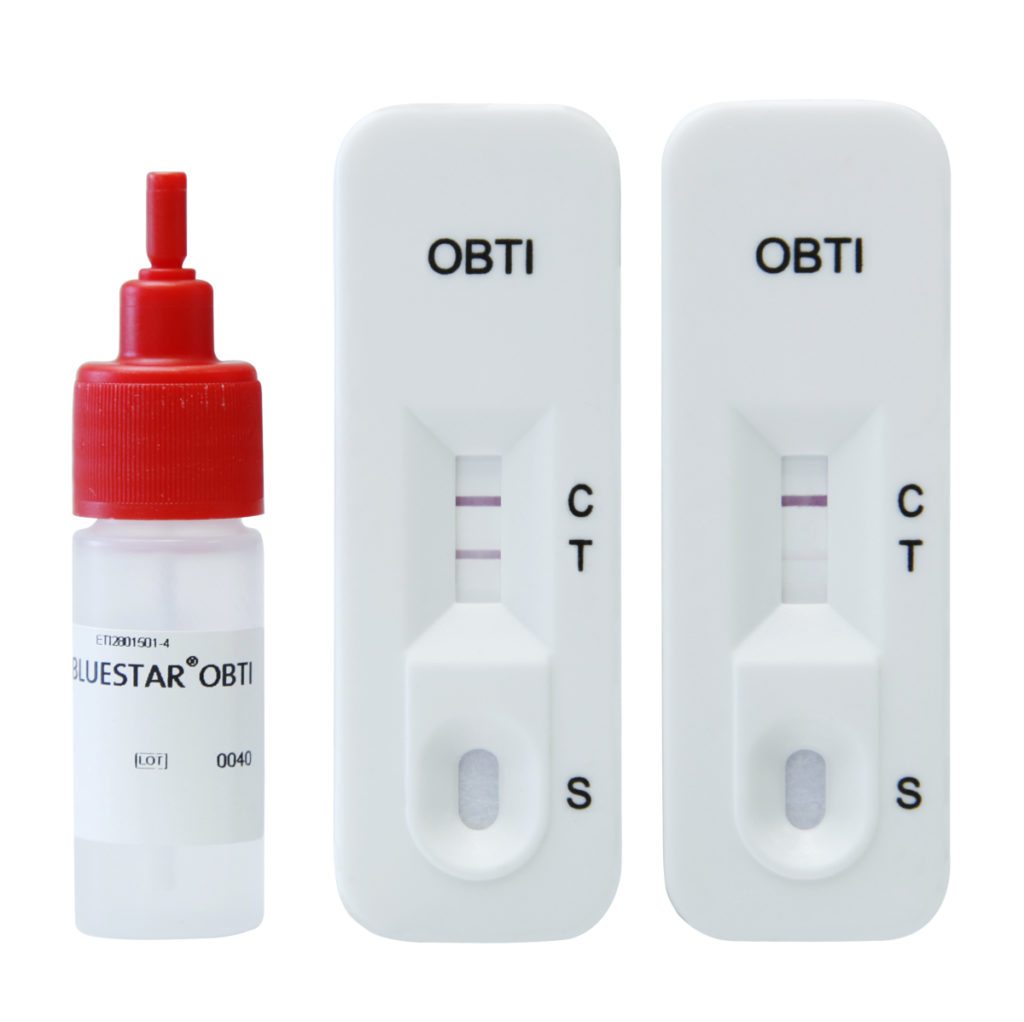
“To identify the presence of blood that cannot be seen with the naked eye, because the scene was cleaned before the police arrived, the forensic police use Bluestar to reveal the erased traces”

Television loves forensics, because there are crimes, investigations, motives, and we get to see the daily lives of police officers and forensic scientists.

A short history of forensics
Before the first tools of forensic science, testimonies and confessions were the basis for convincing a suspect of his guilt. Alphonse Bertillon (1853 – 1914) founded the first police laboratory for criminal identification in 1882. He constituted the basis of forensic anthropometry, which allows the identification of people.
Ten years later, Francis Galton introduced systematic identification by fingerprints. Other valuable tools in a criminal case are the presence of traces, photos of the scene and a map of the scene. The forensics team makes observations at the scene, verifies and cross-checks the information gathered. It uses all techniques to materialize the facts.

In which cases does the forensic science department intervene?
The daily work of the forensic police of Poitiers is to intervene – in the order of the number of cases – on burglaries, robberies, discovery of stolen vehicles, corpses (found on the public highway, unidentified, suspicious deaths…), violence to persons, damages, fatal accidents, work accidents, rapes and drug trafficking.

In France in 2020, the police made 350 000 interventions and 50 000 identifications. In Poitiers, they made 2,000 trips and 250 identifications.
The forensic police look for material evidence following a very precise protocol. At the scene, they start by taking pictures to freeze the scene, look for traces and clues, install riders (these small numbers that identify the objects in the scene on the pictures) and take samples (objects, weapons).
The tools of forensic science
A number of samples are taken from a crime scene and from the suspect(s): fingerprints, hair, semen, gunshot residue on the shooting hand, presence of blood. To identify the presence of blood that is not visible to the naked eye, because the scene was cleaned before the police arrived, the forensic science team uses Bluestar to reveal the erased traces. The luminol makes the iron in the blood react.
The Poitiers crime lab is a pilot site in France for the digital forensics service.
external examination of the body to determine ante-mortem and post-mortem trauma. The autopsy is an opening of the body to identify types of trauma, violence, blows, to take samples, to see the state of the lungs (in case of drowning) and to identify a body in bad condition, by taking a sample from the femur. The forensic pathologists will submit a forensic autopsy report.
DNA is a tool used on a daily basis by forensic scientists, including for burglaries. DNA is often a hope for cold cases, those cases that have remained unsolved for years (like the Grégory case or the Omar Raddad case). To be efficient, it is necessary to have a large quantity of quality samples and a good conservation of the seals, because the enemies of DNA are known: light, humidity, heat, UV rays…
Other Articles

IAI Annual Educational Conference 2023
August 20-26 Maryland BLUESTAR® Forensic will be present at IAI 2023 Located at the iconic Gaylord National Resort in National Harbor, Maryland, from August 20 to 26,

Forensic PSA Test: BLUESTAR® Identi-PSA® – The Essential Tool for Crime Scene
Forensic PSA Test: “BLUESTAR® Identi-PSA®” An Essential Tool in Forensic Medicine for Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Detection In the world of forensic medicine, speed and accuracy

Rose Petal Murder: The Case Involves the Use of BLUESTAR® Forensic Reagent
The brutal murder case of Christina Parcell in South Carolina is drawing national attention and highlights the use of BLUESTAR® Forensic, a blood detection solution.

BLUESTAR® at the 75th AAFS Conference
American Academy of Forensic Sciences 75th Anniversary Conference The American Academy of Forensic Sciences is celebrating its 75th anniversary by hosting the conference entitled “Science

Chemical indicates the presence of human blood in the trailer
After detectives photographed the inside and took some items into evidence, they cleared the floor in order to apply a chemical known as Bluestar, which

KU Leuven Students Investigate Virtual Crime Scenes
Investigating murders as a forensic expert… (India Education : Apr 26, 2022) Taking DNA samples, making blood traces visible with a chemiluminescent spray (‘Bluestar’) or

Forensics, the latest methods
When pollen and insect larvae are used to solve criminal cases and even historical enigmas… This documentary takes a look at the fascinating resources of

How does the scientific police work?
How does the scientific police work?(Le Mag de France Bleu Poitou) (France bleu: January 21, 2022) “To identify the presence of blood that cannot be
Forensic science, clue hunters
Tarbes: Scientific police, the clue hunters La nouvelle république des Pyrénées : November 4, 2021 The technical and scientific police of Tarbes opened us the

Lemerle case: traces of blood revealed by Bluestar
On the first day of Vanessa Lemerle’s trial for the violent confinement of her brother Le quotidien : October 26, 2021 On the first day

A state-of-the-art portable crime lab
Costa Rica’s First Female Forensic Biologist Designed a State-of-the-Art Portable Crime Lab MENAFN : 18.09.2021 In 2010 Tatiana López had to present a University project, she was
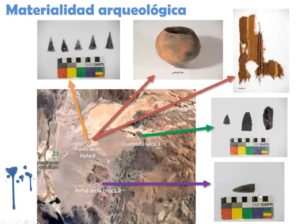
“With the blood in the eye” Bioarchaeology and Biomaterials.
“With blood in the eye”. Romano et al. Axis 1 – Bioarchaeology and Biomaterials. Presentation of the paper “With blood in the eye”. Revealing and

Canine Handlers and Forensic Specialist Testify in Smart Hearing on 2021 Searches
Canine Handlers and Forensic Specialist Testify in Smart Hearing on 2021 Searches Neither cadaver dog made strong alerts to seized Volkswagon or Ruben Flores’s property

IAI Annual Educational Conference
Find us at the IAI Annual Educational Conference Nashville August 1-7 Booth 225 Our team will be present at the IAI 2021 conference in Nashville. We will

Troadec case: traces of blood, burning of the bodies, the word of the experts.
The trial of Hubert Caouissin and Lydie Troadec continued with the testimony of experts who worked on the case. France info : 29.06.2021 The trial

Alleged serial killer: new excavations and Bluestar in the orchard
Could the crime scene at Mare-d’Albert be hiding other sordid secrets? In any case, this case, which has been in the news since Friday 28

Police brought Agostina’s alleged femicide to Neuquén
A commission of the local police force transferred Juan Carlos Monsalve from Viedma, accused of being the perpetrator of the femicide. Agustín Martínez LMCipolletti :

Detecting Blood in an Outdoor Environment with the Bluestar Reagent and DNA Analysis
Author(s): McCall, Keenan; Woods, Grace; Richards, Elizabeth Type: Article Published: 2021, Volume 71, Issue 4, Page 309 Abstract: Blood is an important physical material that

Thomas Lesire trial: These clothes are examined with Bluestar reagent
Assizes: trial of Thomas Lesire, accused of the murder of an octogenarian in Châtelet, begins RTBF 03.05.2021 The neighbourhood investigation led the police to a

Daval case: investigation and use of Bluestar
Daval trial: life sentence requested against Jonathann Daval accused of a “terrible” crime, relive the sixth morning of the trial L’est Républicain : 21.11.2020 “When

Case of a missing youth: raids and investigation procedures continue
The procedure was carried out jointly with police personnel from the Forensic Science Department and the 43rd Central Police Station of Jhugua Ñaro and the


Galveston AA group leader’s killer is still out there after 2 years
Galveston AA group leader’s killer is still out there after 2 years ABC 13 : 29.06.2020 [United-States/Texas] Donna Brown walked into the Alcoholics Anonymous building

He had tried to erase the trace of the victim’s blood
The baby was beaten and tortured, recorded in bruises, scratches, burns and fractures from the brain down. Photo: Jenny Rocio Angarita Galindo (Radio RCN) Alerta

Policeman’s Memory : a barbaric crime!
By Fadel ATAALLAH – POLICE magazine N° 57 Octobre 2009 This article reports on a criminal case solved by senior police officer Abdelmoula Choukrallah, head

Narumi case: investigators accuse the main suspect
The Chilean ex-boyfriend of this Japanese student who disappeared in Besançon in 2016 fled to his country. The French justice has just revealed accusing elements

Christine Wood’s DNA found in Brett Overby’s basement, court says
CBC NEWS : 02.05.2019 Christine Wood’s blood was found on a weight bench, closet door and stairs in the basement of a Burrows Avenue home
Bluestar, the miracle product that solves many criminal investigations
Bluestar, which was developed in a CNRS laboratory, has become an essential tool in complex investigations and a formidable weapon in the hands of the

Justice for the Lyon Sisters
How a determined squad of detectives finally solved a notorious crime after 40 years For decades, the disappearance of Sheila and Kate Lyon wasn’t just

Jealous husband in South Africa kills his wife’s lover.
Jealous husband in South Africa kills his wife’s lover.

Murder of a woman by her son
This matricide was solved by the French Gendarmerie Nationale using BLUESTAR® FORENSIC. The woman had been missing for 15 days. BLUESTAR® FORENSIC was sprayed in

Alexia Daval case: other acts and hearings to come
L’est Républicain : 07.07.2018 New forensic expertsAbout forty experts of all kinds have already worked on the case: no less than five forensic doctors; several

JESSIE BARDWELL CASE: WAS TEXAS WOMAN’S DEATH AN ACCIDENT OR MURDER?
A father dreams his daughter has been killed, then she disappears — what does her boyfriend know and could the dad’s nightmare have been an

They capture the partner of a mannequin
The subject claimed that when he arrived at the apartment he found the woman dead, but technical evidence contradicts this version and indicates that he

Scientific advances have made a blood trail speak for itself
Maëlys: how scientific progress made a microscopic trace of blood talk FRANCE 3 : 09.12.2019 They escaped the meticulous cleaning of Nordahl Lelandais. Then, at

Invisible bloodstains revealed by Bluestar
Mallouk case: the long trial of a murder without a confession (FRANCE 3) Hafid Mallouk is to be tried for a fortnight for the murder

A matter of gold and blood
BEHIND THE DISAPPEARANCES OF ORVAULT, THE TROADECS’ FAMILY TRAGEDY (France Info story) A blue and white column slowly progresses through a wooded and soggy landscape.

Killer of elderly woman confesses he had help from hitman
Puno: the killer of an old woman confessed to having been helped by a hitman Diario Correo : 27.05.2017 He killed his wife because he

The murderer of an old woman confessed to having been helped by a hitman
Puno: the murderer of an old lady confessed having been helped by a hired killer Diario Correo : 27.05.2017 He killed his wife because he

The scene of a crime, suicide or natural death has no mystery for the “cleaners”
It’s a job that is rarely mentioned, as if to ward off bad luck. The very mention of it brings to mind crime scenes seen

Improved detection of Luminol blood in forensics
Review: Improving Luminol Blood Detection in Forensics Florida Forensic Science : 01.03.2017 (Emily C. Lennert) Article to be reviewed: 1. Stoica, B. A. ; Bunescu,

Officers get forensics training
A couple dozen first responders and crime scene investigators gathered around a makeshift crime scene Wednesday afternoon in Jackson. Jackson Sun : 31.12.2016 They watched

Photographing bloodstains
Photographing bloodstains: Bluestar reagent FORENSICS 4 AFRICA 07.07.2016 (Nick Olivier) In the late summer of 2012, police officers in a small Midwestern town were called

Mystery around a disappearance
Yves Bourgade’s murder: BLUESTAR® FORENSIC strengthens suspicions about his wife…

Nisman case: the conclusions of the criminal report
Nisman case: conclusions of the official criminal report point to suicide 11.06.2015 – ARGENTINE – INFOBAE – Infobae has accessed the 97-page document that

Traces of blood were found in his marital home, revealed by the “Bluestar”.
Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Share on pinterest Share on reddit Share on vk Share on tumblr Share on telegram Share

The judge in the Yexeira case accepts as evidence another piece with blood on it.
To complete the process of authenticating the evidence, the magistrate noted that the other ICF staff member who received the evidence for analysis would also

20 years of forensic bloodstain analysis in Ontario
While University of Windsor students play with spatter at a forensics conference, provincial police mark the 20th anniversary of bloodstain pattern analysis in Ontario. (Dax

Chief Warrant Officer Benitez left a bloody trail
The clues are accumulating around Chief Warrant Officer Benitez and his involvement in the disappearance of Allison and her mother Marie-Josée on 14 July in

The Flactif case: An investigation solved with Bluestar
At a crime scene, he makes the bloodstains talk “When I entered the Flactif house, I immediately noticed the traces of sponge strokes in the

Photographer Exposes Crime Scenes, With a Dash of Chemistry
Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Share on pinterest Share on reddit Share on vk Share on tumblr Share on skype Share
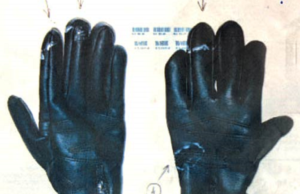
Bloody gloves in Israël
Bloody gloves “catch” Israeli attorney Anat Plinner’s murderer…

Forensics, how does it work?
Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Share on pinterest Share on reddit Share on vk Share on tumblr Share on skype Share

Flactif, The cursed cottage is for sale
The parents of Xavier Flactif, massacred with his family in April 2003, have returned to the scene of the tragedy. The chalet of Grand-Bornand, in

The blood of two confederate soldiers revealed at Gettysburg
Gettysburg Civil War case revealed after 142 years !
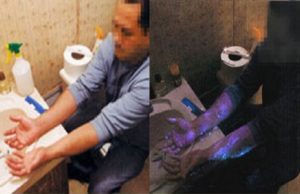
Suspect arrested on crime scene after his arms turn blue !
A man arrested after his arms turn blue…

The secrets of real experts (LE FIGARO)
Philippe Esperança, morpho-analyst: Blood on the trail By Le Figaro, 21/07/2006. “Espé” is the French specialist in the revelation and analysis of bloodstains. At the

The Flactif case: With Philippe Esperança
BLUESTAR® FORENSIC helped solve the Grand-Bornand quintuple murder case The Flactif family had mysteriously disappeared from their chalet. The programmes “Faites entrer l’accusé” and “Secrets

Shooting of a pedestrian by a driver
A driver shoots and kills a pedestrian…